UNST 220 Understanding Communities
Dr. Martha J. Bianco
Module I Lecture Guide
Part I
Polis, Metropolis, Megalopolis:
From Urban Specks to Global Cities
Click
here to download a printable pdf version of this lecture guide.
You'll need Adobe Reader, which you can download for free by clicking on the
icon below:
 .
.
I. Introduction
II. What is a City?
|

|

|

|
|
Image from 1926 film Metropolis, set in
year 2000
|
Image from 1982 film Blade Runner (Tyrell
Corporation), set in 2019
|
Image from 1995 television series Star Trek
Deep Space 9 (Bajor, United Federation of Planets) set in 2370
|

III. Cognitive
Map
IV. The
Study of the City
A. Urban
studies
B. Different
paradigms for different disciplines
V. Theories
of Urbanization: Where and When Was the
First City?
|
|
|
Map of Ancient
Civilizations
|
1. V. Gordon Childe (1892-1957) was an
Australian archaeologist who studied the rise of civilization.
a. the
agricultural revolution
b. the
urban revolution
mastery over nature  agriculture
agriculture  surplus
surplus  development of city
development of city
2. P
O
E
T
3.
Cities of the
Fertile Crescent
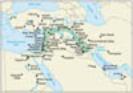 Map of the Fertile Crescent
Map of the Fertile Crescent
Factors
Making Them Cities, According to Childe:
a.
size & density
b.
diversity & specialization
c.
monuments & ruling class
d.
trade
e.
science & art
f.
writing
B. Other
Early Cities
1.
Jericho
2.
Old Jericho
3.
Çatal Hüyük /
Çatalhöyük
4.
Tell Hamoukar
|

|

|

|
|
Tell Lidar (photo)
|
Tell Megiddo (model)
|
Tell Megiddo (color
reconstruction)
|
C. Jane
Jacobs' Trade / “New Obsidian” Theory
desire to carry on trade  city settlement
city settlement  agriculture
agriculture
D. Lewis
Mumford and the Sacred Meanings Thesis
desire to have fixed holy
landmarks  city settlement
city settlement  agriculture, trade, diversification, science
etc.
agriculture, trade, diversification, science
etc.
VI. CLASSIFYING
CITIES
A. Gideon
Sjoberg’s Classification of Cities
1. Preindustrial City
2. The Industrial City
VII. Concepts of Community
A.
Gemeinschaft
B.
Gesellschaft
C. Techno$chaft
VIII. A
TOUR OF WORLD CITIES
|
|
|
Virtual Tour of
Ancient Cultures
|
A.
THE RIVER’S EDGE: The
Role of the River in Ancient Cities
1.
Cities of the Fertile Crescent: Rivers Forming the Cradle of Civilization
|
|

|

|

|

|

|
|
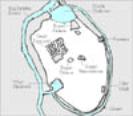
Map of Ur
|
Color
reconstruction of Ur
|
Ziggurat
|
American soldiers
on ziggurat in Ur
(Iraqi War 2004)
|
American soldiers
on ziggurat in Ur
|
Artist’s
reconstruction of dwelling in Ur
|
2.
The World of the Nile:
A Civilization Devoted to the Gods
|

|
|

|
|
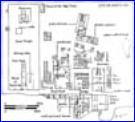
Map of Akhetaten
(1349 BC)
|
Main city of
Akhetaten
|
Black & white
reconstruction
|
|

|

|

|
|
Color
reconstruction of Akhetaten
|
Aerial view of
Akhetaten
|
Pharaoh Aketaten and Nerftiti worship Aten
|
|

|
|

|
|
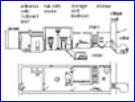
Workers’ settlement
|
Worker’s flat
|
Noble’s residence
|
3.
Around the Huang Ho River: A Rigidly Stratified Society
 Plan of capital city of Ch’ang,
from 7th Century
Plan of capital city of Ch’ang,
from 7th Century

B. THE FORTIFIED EDGE
1. Dwellings as Protection in Çatal Hüyük
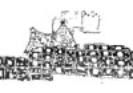
|

|

|
|
Early wall painting
from Çatal Hüyük
|
Black & white reconstruction of Çatal Hüyük
|
Color
reconstruction
|
|

|

|

|
|
Çatal Hüyük from
above, showing laddered entrances into dwellings
|
Individual dwelling
|
“Suburbs” of Çatal
Hüyük
|
C. MULTIPLE
EDGES
1. City within a City:
The Greek Polis
a.
acropolis
b.
agora
|
|

|
|
|
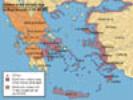
Map of ancient Greece
|
Acropolis of Priene
|
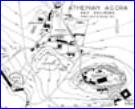
Schematic of Athenian
acropolis and agora
|
|

|

|

|
|
Schematic of Athenian
agora
|
Map of Athenian agora with
acropolis in background
|
Model of Athenian agora
|
|

|

|

|
|
Model of Athenian acropolis
and agora
|
Black & white
reconstruction of agora
|
Color reconstruction of
agora
|
2. The Fortified City: Protecting the Medieval Economy
a.
burgs (boroughs)
b.
organic towns
D. BEYOND
THE EDGE
1. Ancient Suburbs
2. Medieval Faubergs
E. CITIES
WITHOUT EDGE: American Settlement
Patterns
1. Key Factors Affecting American
Settlement Patterns
a. natural
resources
b. values
and beliefs
 freedom
freedom
 individuality
individuality
 mastery over nature and over other
peoples
mastery over nature and over other
peoples
 capitalist economy
capitalist economy
 emphasis on economic growth
emphasis on economic growth
 social valuation of space
social valuation of space
 egalitarianism
egalitarianism
 right to privacy
right to privacy
 expansionism
expansionism
2. How These Factors Have Affected
American Settlement Patterns
3. The Edge City
a.
more than 5 million square feet of office space
b.
at least 600,000 square feet of retail space
c.
more jobs than homes
d.
“has it all”
e.
did not look anything like a city 30 years prior

Click to see an animation of
Tyson’s Corner, Virginia, as it develops from 1937 to 1990










Click on each photo
individually to view it without animation.


Washington Square, Progress, Beaverton-Tigard Area,
Oregon, before and after construction of square in 1974.
Additional Reading:
Fraim, John.
“Cultural Places.” Symbolism of Place. (2001). <http://www.symbolism.org/writing/books/sp/3/home.html>.
Garreau, Joel.
“Edgier Cities.” Wired 3:12 (1995) <http://www.wired.com/wired/archive/3.12/edgier.cities.html>
Geddes, Robert.
“Metropolis Unbound: The Sprawling American City and the Search for
Alternatives.” The American Prospect 8:35 (1997) <http://www.prospect.org/print/V8/35/geddes-r.html>.
Mitchell, John
G. “Urban Sprawl.” National Geographic Magazine Online (2001).
<http://magma.nationalgeographic.com/ngm/data/2001/07/01/html/ft_20010701.3.html>
Putman, Robert
D. “The Strange Disappearance of America.”
The American Prospect 7:24 (1996) <http://www.prospect.org/print/V7/24/putnam-r.html>.
Tönnies,
Ferdinand. Community and Society: Gemeinschaft und Gesellschaft.
Reprinted in and translated by Charles P. Loomis, 223-231, Michigan State
University Press. 1957. In Marcello Truzzi. Sociology: The Classic
Statements, 145-154. New York: Oxford University Press, 1971. < http://www2.pfeiffer.edu/~lridener/courses/GEMEIN.HTML>.
Online Experiences
Schneider,
Bernd. “Galleries – Planets and Cities.” Ex Astris Scientia: Bernd
Schneider’s Star Trek Site. <http://www.ex-astris-scientia.org/gallery/planets1.htm>.
“Blade Runner:
The Replicant Site.” <http://www.blade-runner.it/>.
“SurrealPlaces
3D Image Galleries.” <http://www.surrealplaces.com/>.
Take a virtual
trip of ancient civilizations, at “Virtual Trip: Introduction to Ancient
Culture.” <http://www.taisei-kodaitoshi.com/civil_e/civilization.html>.
Explore
ziggurats, tombs, and palaces and play ancient board games and take other
“challenges” at the British Museum’s website:
Mesopotamia: The British Museum. <http://www.mesopotamia.co.uk/>.
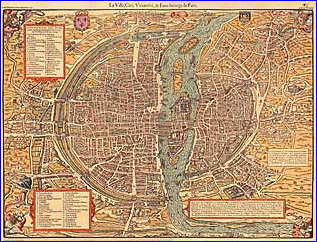
Explore the
highly detailed interactive map of 16th century medieval Paris, by
François de Belleforest (1572), at <http://www.paris.org/Maps/Map2>.
“Virtual World:
The New Suburb?” NationalGeographic.com. 2001. <http://www.nationalgeographic.com/earthpulse/sprawl/index_flash.html>.
“Tour.” Congress
for the New Urbanism <http://www.cnu.org/about/index.cfm?formaction=tour&CFID=8133658&CFTOKEN=1187455>
“Suburban
Sprawl Slideshow.” Christian Science Monitor. <http://www.csmonitor.com/slideshows/durableSlideshows/suburbanSprawl/slide1.html>.
“Contested
Narrative: The Contest over Who and What to Believe.” Globalization Research
Center. 2002. <http://www.earthwindow.com/grc2/narrative>.
“The Venus
Project: A Redesign of the Future.” <http://www.thevenusproject.com/>.
©
Martha J. Bianco, Ph.D.
2004-2005
![]() .
. ![]() agriculture
agriculture ![]() surplus
surplus ![]() development of city
development of city Map of the Fertile Crescent
Map of the Fertile Crescent![]() city settlement
city settlement ![]() agriculture
agriculture![]() city settlement
city settlement ![]() agriculture, trade, diversification, science
etc.
agriculture, trade, diversification, science
etc.